What is
Refractive
Error?

Refraction is the scientific term for the bending of light as it travels through one object to another. Vision happens when light rays are bent or refracted as they travel via the cornea and the lens. Light is trained on the retina, which converts the light-rays into signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain then translates these signals into the images we see.
A refractive error is one of the most common eye disorders. It means that the eye's shape does not bend light correctly so that it cannot focus on the right area of the retina. This results in blurred or unfocused images.
Thank you
We’ll get back to you soon.
What are the causes of
refractive error?
The eyeball's length being too short or too long is one of the cause of a refractive error is an irregularly shaped cornea. As people age, the ability to focus up close also becomes difficult because of the greater rigidity of the ageing lens.

What are the types of refractive error?
There are many different types of refractive error, all of which can vary among individuals as to the degree of severity. Here are the most common:
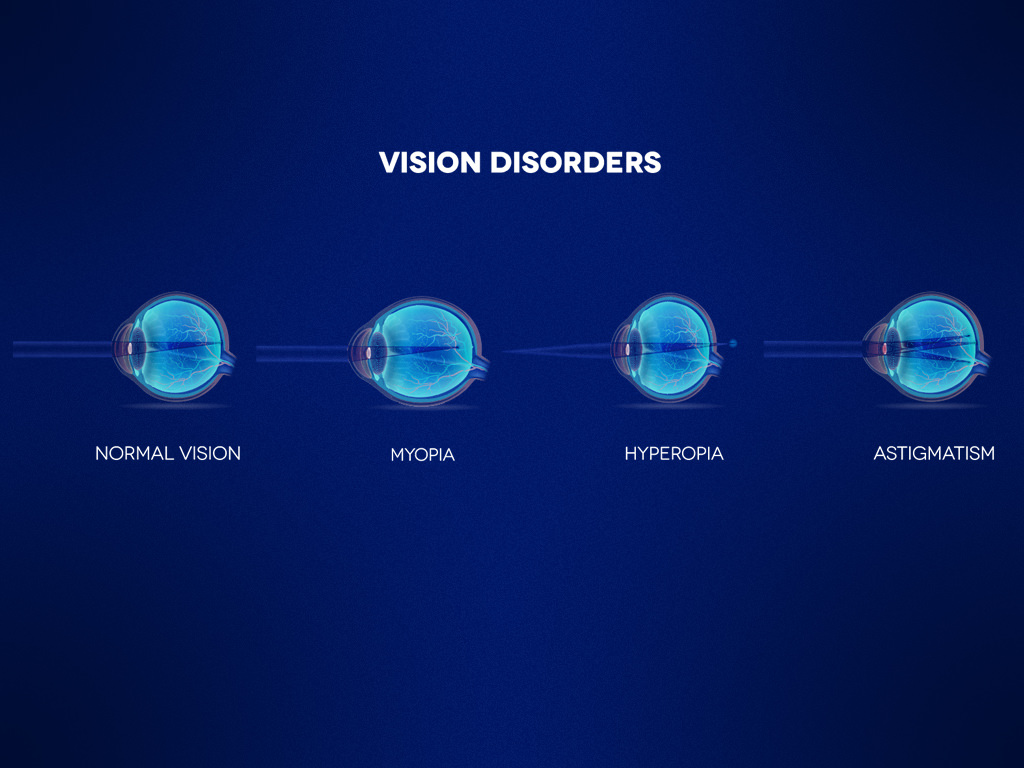
Myopia (short-sightedness)
Light focusses in front of the retina rather than on it. This means that far away objects are blurred and indistinct but nearby objects are clearly visible. Untreated myopia can cause headaches as a result of eyestrain, and squinting - the need to partially close the eyelid to try and see.
Astigmatism
This is a condition where light fails to focus on a single point on the retina, resulting in blurred or stretched-out vision. Double vision, headaches are common symptoms of astigmatism.
Hyperopia (far-sightedness)
This is a form of refractive error where light focuses behind the retina rather than on it. People with hyperopia can see objects at a distance but have problems focussing on things that are close up. This is a condition that is likely to worsen with age.
Presbyopia
This is an age-related refractive error where the lens is no longer flexible enough to change shape and allow the eye to focus clearly on near objects.
Refractive Error F.A.Q's
How is refractive error diagnosed?
An optometrist will diagnose a refractive error following a detailed eye examination, which is completely painless and non-invasive. People usually make an appointment for an eye test after experiencing problems with their eyesight. However, sometimes a refractive error is diagnosed during a routine check-up and the patient has been unaware of any problems with their vision.
How is a refractive error treated?
An optician will make an eyeglass prescription and then the patient can either choose to have glasses or contact lenses. Glasses are suitable for all patients and modern contact lenses can also be worn by most people, although older people with drier eyes may find that they can only wear them for short periods. Another option is laser eye surgery which is a highly effective way of correcting many types of refractive error.
Thank you
We’ll get back to you soon.
How can you prevent refractive error?
Recent research suggests that a lack of sunlight in early childhood and the teen years can increase the risk of myopia so ensuring children spend plenty of time outside seems a sensible precaution. In the past, some people believed that it was possible to correct refractive errors by performing regular eye exercises, but there is no evidence to suggest there is any benefit to doing this. Unfortunately, there is no scientifically proven way of preventing a refractive error; it is either a genetic or an age-related condition. The good news is that visual impairments caused by a refractive error can usually be completely corrected.
It cannot be emphasised enough how important it is to have your eyes tested regularly. For more information about refractive errors and any other eye problems and conditions, please contact the Orbit Eye Hospital in Mumbai, which provides an extensive range of high-quality ocular treatments.
